
Research area focuses on animals, plants and microbial genomes to identify potential genetic determinants involved in organism’s adaptation to different environment condition, i.e. natural, modified, or linked to human requirements. Genetic studies are based on the use of wet and in silico molecular approaches, statistical analysis of molecular data and collection and processing of Big Data, applied to biological systems of agricultural interest such as structural and reproductive biology, evolutionary genetics and germplasm conservation. Advanced technologies and bioinformatics tools are also used for the collection and examination of semen for the preservation of genetic resources.


GENOBU is an original, innovative and multidisciplinary project combining genome sequencing of the water buffalo to the healthiness of animals and the improvement of quality and quantity of buffalo food products. The project will develop know-how and innovative process technologies to be provided to breeders and agro-food industry, with the objectives of optimizing the efficiency in milk processing, and to ensure best nutraceutical value to buffalo foods.


The project is aimed at the genotyping, through plastid and nuclear molecular markers (TBP), of the whole collection of small aquatic macrophytes (Lemnaceae) known under the name of Landolt Duckweed Collection and currently managed by Dr Lammler in Zurich. This historical collection, the largest in Europe, includes about 500 clones of the 36 known duckweed species, coming from five continents. Accessions have been mostly characterized on a morphological basis, which may cause a high rate of misclassifications in some species, owing to the simplified structure of these tiny plants and the high similarity between some species.
Since long used as environmental bioindicators, duckweeds and renowned for their phytoremediation capacity. Due to their extraordinary fast growth, duckweeds are one of the most promising new crops, under intensive study for energy production and as a source of high quality proteins for animal and human nutrition, already under evaluation as a novel food by EFSA.
Results will be useful to:


BIO4VERBA project arises from the need of the breeders of the Verzaschese and Bionda dell’Adamello goat breeds to preserve and enhance their local breeds and the relative products.
BIO4VERBA has the following objectives:
5. Support breeders who prefer grazing, through a characterization of their products (Formaggella del Luinese PDO and Fatulì of the Saviore Valley) that allow to identify the contribution of grazing to the sensorial cheese properties (characteristics of cheeses).
The CASTANEVAL project intends to respond to the need for scientific knowledge on Lombardy chestnut genetic resources in order to provide tools for the leverage and conservation of native germplasm and to undertake actions for the management recovery of chestnut groves. The pilot study areas are the chestnut groves in the municipality of Serle (BS) and in the Varese Pre-Alps (VA) The CASTANEVAL project aims also to develop a chestnut micropropagation system in order to offer a concrete, sustainable and economical tool for the conservation and multiplication of native germplasm of high local interest. The project will also study the ecological context and the degree of naturalness of the stands, from wild to coppice and cultivated varieties. A complete characterisation of the chestnut genetic resources in the areas under consideration will result from the integration of genetic, morphological, ecological and production data.


The adoption of agronomic practices aimed at maximizing production yields led, during the 20th century, to a drastic change in the characteristics of cultivated varieties toward specific characteristics of the final product and plant architecture.
So-called “old” varieties are sometimes considered capable of providing productions with better quality, organoleptic and health characteristics than those provided by modern varieties bred under intensive agronomic conditions.
The TRANFER project aims at the valorization of historical maize and wheat varieties typical of the Lombardy region through molecular, biochemical and phenotypic approaches. In particular, traits of interest related to resistance to fungal pathogens, characterization of seed morphology and nutraceutical qualities will be studied.
TRANFER will provide information on the diversity that exists in Lombardy’s germplasm collections for its valorisation and use in local production


The Microbial Resource Research Infrastructure (MIRRI) is the pan-European infrastructure in charge of preservation, analysis, supply and exploitation of microbial resources and biodiversity. The project SUS-MIRRI.IT aims to develop research, services and training within the Italian network of culture collections MIRRI-IT, which will preserve biological diversity, collect and store data associated with microorganisms, carry on research and provide external users with support and services related to microbial resources. The optimised management of the bioresources at the MIRRI-IT Research Infrastructure, coupled with the digital platform and data handling/sharing strategy will allow the exploitation of microbial biodiversity and provide innovative solutions and products of biotechnological interest, stimulating the bio- and circular economy.
The IBBA Pisa unit participates with the microbial culture collection MLIP (Microbiology Lab IBBA Pisa), including microorganisms originated from different environmental and food sources.


The project will focus on technology-driven breeding methods for the genetic improvement of crops (breeding 4.0) in diploid (barley, Hordeum vulgare) and polyploid (durum and bread wheat, Triticum durum, aestivum) species to increase cereal production in a sustainable and climate-smart way. Target technologies are high throughput phenotyping (e.g. drone phenotyping, root scans from rhizotrons) and genotyping (e.g. SNP array, exome sequencing, GBS) for artificial intelligence based breeding. Phenotypes will include yield, morphometric measurements, UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle: drone)-captured image data linked to morphology and production efficiency and rhizotron-based root scans (both 2D and 3D). Machine-learning methods, focussing especially on deep learning methods, will be used for phenomic and whole-genome predictions of target phenotypes.


Sheep-TreeSeq will perform scalable analysis of genomic diversity of sheep global populations using the novel tree sequence data format and methodology.
Technological advances in agritech have increased the availability of genomic data, leading to massive datasets (“big data”) which pose challenges for storage, processing and analysis, e.g. the sheer volume of the data, the rapid generation of new data (updating results, expanding training populations, streaming applications), and the heterogeneity of data sources (integration of data from multiple sequencing and genotyping platforms). The tree sequence algorithm offers an excellent way to address such challenges, by providing lossless compression and novel representation of the data. As an example, using tree sequences on the 1000 Bull Genome Project data a 90% lossless compression was obtained, reducing the data size from ~800 GB to 45 GB. For the Sheep TreeSeq project we will use around 3,500 sheep whole genome sequences and over 50,000 genotypes (~10 TB of data).
Our plan is to apply the tree sequence approach to compress the data and obtain a data representation highly suited for population genetics and demographic analysis: (i) principal component and genealogical nearest neighbour clustering; (ii) fixation index measuring genetic differentiation; (iii) deep neural network based clustering methods; iv) detection of runs of homozygosity (ROH) and heterozygosity-rich regions (HRR).
This is the first time that this approach is applied to sheep genomics.


The INF-ACT research program addresses pressing unmet needs of human emerging infectious diseases in both fundamental as well as in translational aspects, taking into consideration human health in a wider context including domestic and wild animals as potential disease reservoirs and environmental factors enhancing the possibility for spillover (One Health approach).
The project is focused on three “vertical” research nodes
and two “transversal” research nodes to interact with the basic and translational activities
The INF-ACT consortium is composed of 25 research Institutions from the public and the private sector from all over Italy; the CNR is involved in Node 1, 3, 4 and 5.


The SCALA-MEDI project will optimise the sustainable use and conservation of local breeds of chicken and sheep from the Mediterranean region, focusing on adaptation to climatic conditions and consumer preferences .
The expertise and data from previous EU projects will be extended to the genetic and epigenetic characterisation of local resources and their adaptation to different production environments in three North African countries, Tunisia, Algeria and Morocco.
Tools and strategies will be developed to improve local breeds for sustainable production. Application of these tools will be demonstrated to farmers in diverse Mediterranean production systems.


Resilience of agricultural and forest ecosystems under stressful conditions generated by climate change (CC) requires valorization and exploitation of genetic resources through cutting-edge conservation strategies, combined with deep characterization of genomes and high-throughput phenotyping.
Activities will include massive sequencing of accession/breeds/strains, extensive marker-based description of genomes, (pan)genome elucidation, deep phenotyping and multi-omics characterization.
Resulting information, processed through advanced methods for complex data analysis/interpretation/storage/management, will highlight superior alleles/haplotypes, identify beneficial interactions under a variety of conditions, and define conservation units.
The COVES project will develop and validate a simplified sampling and analysis procedure on a portable device for the specific and sensitive detection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the environment. This procedure will ensure greater safety in the work areas, thus reducing the negative impact that the COVID-19 emergency has on the local and national economy and decreasing the gap between the information and the suggested solutions. The main result of the project will be the development of a method for the rapid analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 in the environment, suitable for a field-use also by non-expert users. The project involves Hyris Ltd, leader of the project, which develops the technology, IBBA CNR which will take charge of the method validations and IZSLER (section of Pavia) which will validate “in-situ” the efficacy of this method on various contaminated surfaces using SARS-CoV-2 positive samples with known concentration.




Il progetto si articola in tre step:
1) L’avvio di un’iniziativa volta al sequenziamento del genoma di frumento duro; l’obiettivo sarà perseguito attraverso strategie complementari che, nel loro complesso, permetteranno di affrontare le due principali problematiche associate al sequenziamento del complesso genoma di questa specie (presenza di due genomi altamente simili e alta percentuale di sequenze ripetute).
2) La caratterizzazione a livello proteomico e metabolomico delle varietà utilizzate per gli studi di genomica. I risultati di questa analisi saranno integrati con quelli prodotti dall’analisi genomica, evidenziando la presenza di eventi post-trascrizionali e post-traduzionali nella biosintesi delle proteine e fornendo indicazioni sulla attivazione di specifici percorsi metabolici.
3) La fenotipizzazione di 150 accessioni già genotipizzate (profili SNP) e derivate tramite Single Seed Descent da landraces/ecotipi. Questa collezione è conservata presso la sede di Bari dell’Istituto di Bioscienze e Biorisorse del Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche. Questi materiali consentiranno la realizzazione di una analisi di mappatura per associazione tra gli SNPs e le caratteristiche morfo-fisiologiche delle piante, fornendo quindi le basi per l’utilizzazione di queste risorse genetiche nella costituzione di nuove varietà di frumento duro.


The FILAGRO project aims to provide solutions to several issues that are emerging in the field of modern agriculture. They concern: production sustainability, biodiversity and environment preservation; improvement in food quality, safety and healthy and nutritional aspects; technology development in favor of industry; new knowledge dissemination. These issues are highlighted as of high importance in the EXPO 2015 and Horizon 2020 programs as well as in the 2013-2015 plan of the Agriculture Directorate of the Lombardy Region.




Collection, evaluation and conservation of genetic material of the Burlina cattle breed as a back-up in the medium and long period in the event of extinction of the breed or the onset of genetic problems in the breed (loss of genetic lines, excessive inbreeding, etc.). The preserved genetic material consists mainly of semen cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen and blood for future DNA extractions.


The aim of the project was the management of the genetic variability of the local Italian sheep and goat breeds through the choice of donors to be stored in the Cryobank and therefore the collection and conservation of their genetic material. For this purpose, the donors of genetic material to be stored in the Criobank have been identified in the Massese sheep, Langhe sheep, Gentile sheep of Puglia, Garganica goat and Nicastrese goat breeds. The seminal material was then collected using reproductive biotechnologies, such as the extraction of epididymal spermatozoa procedures, that had previously been developed in the IBBA laboratories in Lodi. The material collected in the project can be distributed to breeders for the insemination of the females for proper management of the genetic variability of their herds and more generally of the whole breed.


Pearl millet is a major crop contributing to food security for poor farmers in arid and semi arid regions of the world. The project aims at providing tools and knowledge to accelerate the breeding of new pearl millet varieties with increased nutritional qualities as well as better adaptation to environmental stresses. New phenotyping methods will be used to characterize a collection of 100 pearl millet inbred lines for 1) root system development and interaction with the rhizosphere microbiota and 2) nutritionally important seed compounds: phytic acid and C-glucosylflavones (goitrogen). The impact of certain root phenotypes on agronomical performances will also be assessed in field trials. In parallel, thousands of high quality DNA markers will be produced on the inbred lines for phenotype/genotype association purpose using next generation sequencing technologies. Together, these approaches should lead to the identification of QTLs/genes involved in agronomically relevant root and seed quality traits.




Aim of the project is the development of common bean lines/varieties with an improved nutritional profile (biofortified and low anutinutrients) resulting from a breeding program in which the biofortified and low antinutrients parents have been provided by IBBA-CNR. These lines will be used for the production of innovative products, such as bakery products, pasta or snacks, destined to specific target consumers, such as diabetics, celiac or individuals with iron requirements. To this purpose bean flours will be prepared from genotypes with different compositions in nutrients and bioactive compounds.


ARGENTO project aims at introducing in Italy the new multipurpose oil crop, camelina (Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz), as a valuable source of healthy oil (rich in omega-3) and proteins for animal feeding. Therefore, during this project it will be evaluate the effects of the agronomic management in response to different environments on the final seed quality of newly released camelina lines aiming at optimizing camelina seed qualitative traits for poultry feeding (i.e., quails). In parallel to the optimization of the agronomic management a deep study of the biosynthetic pathway of the glucosinolates (GLSs, antinutritional compound) and also a reduction in GLS content will be carried out by genome editing technologies that enable precise manipulation at a desired location within the genome.
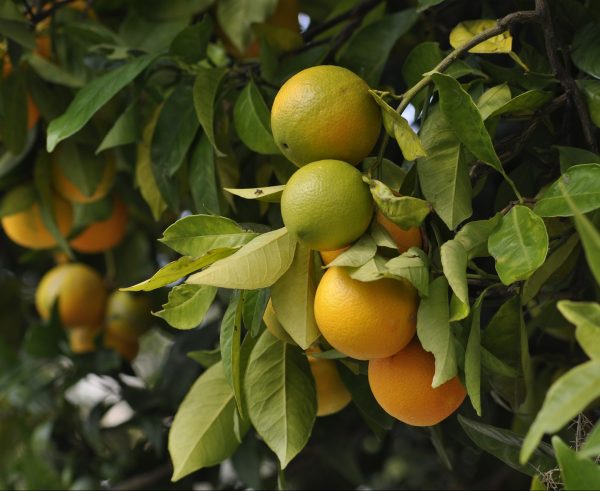


The project aims to identify unique DNA polymorphisms charactering Citrus × myrtifolia, Savona ecotype (Chinotto di Savona) with particular attention to intronic sequences. The goal is to identify single nucleotide polymorphisms specific for the investigated ecotype, in order to genetically characterize it from other ecotypes spread throughout the country, encouraging cultivation and production.


The objective of this project was to analyse how the frequencies of the main casein variants and haplotypes changed in the Italian Holstein breed, and the possible effects on milk technological properties (milks more suitable for dairy processing, with potential greater digestibility). The results obtained by the genotyping (Illumina beadchip) of all the historical data available (over 220,000 Italian Holstein Friesian individuals and over 600 Italian Jersey individuals) were analysed in order to verify how the allele frequencies to the casein genes have been changing in recent years. The results indicate that the increase of the B allele, favourable for cheese-making, and the decrease of the unfavourable E allele at the k-casein are compensating the increase of the A 2 allele at the β-casein, generally maintaining a good proportion of haplotypes associated with good cheese-making properties.


The project, which involves different departments of the University of Milan (DISAA, DIMEVET, VESPA), researchers from the CNR ISPA and CNR IBBA and the DIANA Department of the Catholic University of the Sacred Heart of Piacenza, aims the primary identification of operative practices for reducing the use of antibiotics in the dairy cow herds. During the study, operative protocols already preliminary tested (administration of Aloe arborescens, use of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris in pre and post dipping, molecules to inhibit Prototheca spp) will be validated during the entire lactation cycle of the cows.
This project will allow breeders to take advantages of new nutraceutical strategies and alternatives to the use of antibiotics, to enhance the innate defences and reduce the incidence and severity of mastitis. The validation of an effective protocol for the selective drying of animals would lead to a reduction of the preventive use of antibiotics, in line with what is requested at European level.


Over the centuries, the chestnut tree, cultivated for its fruits and timber, has become an essential element of subsistence for many societies in mountain and sub-mountainous areas, revealing its potential as a multifunctional species. However, today a large part of chestnut forests is in a state of degradation and abandonment, mainly due to the depopulation of rural areas, global climate change and recent outbreaks of exotic pests. With a view to the recovery and enhancement of chestnut genetic resources, the CASTADIVA project mainly aims to:


The complexity of the current global socio-ecological crisis highlights the limits of specialist science as the only voice capable of informing decisions. In the contemporary scenario, where the facts are uncertain, the values in contrast and the stakes are high, the social contract between science, society and politics is in a phase of profound transformation. To face this change, the scientific community has to revisit its social role, creating new relationships not only with society but also with ecological systems, to generate responsible research practices capable of producing relevant knowledge. BRIDGES is a social research project that develops trans-disciplinary and participatory research methods to strengthen the relationship between science, society and ecological systems in the Italian context. To do this, it uses as a case study a specific complex socio-ecological issue, very relevant in Italy: soil fertility.
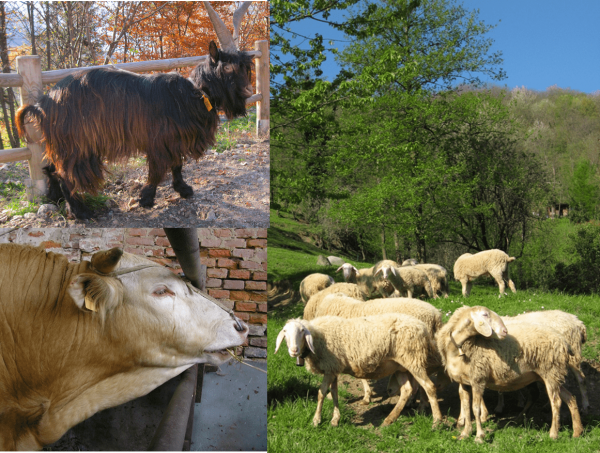


The focus of the project is the conservation and enhancement of a still little known Lombard biodiversity, which risks being lost even before being studied. The project has the following three objectives:
1) expansion of the Lombard Genetic Resources Bank – LABank – launched in 2008, with the addition of new breeds and with the increase of the genetic material of those already present. At the end of the project, LABank 2.0 will be created as a result of the expansion of LABank;
2) creation of the second LABank 2.0 site, to minimize the risk associated with any “catastrophic” events, in accordance with the “FAO Guidelines” (Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources. Animal Production and Health Guidelines No. 12. Complete Book. FAO, Rome p. 222., 2012), with the Piano Nazionale per la Biodiversità di interesse Agricolo (PNBA), emanato dal Ministero delle Politiche Agricole, Alimentari e Forestali e approvato il 14 Febbraio 2008;
3) to develop tools for easy management and enhancement of their breeds, as an important part of the Lombard indigenous animal biodiversity, also in order to preserve and enhance the agro-ecosystems linked to them.
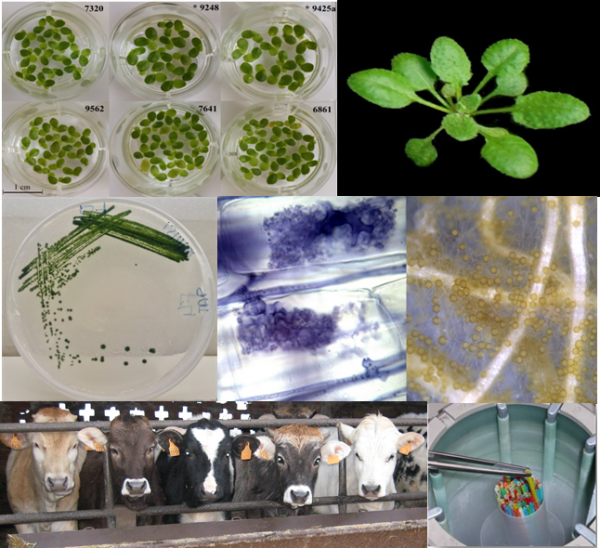


The project is organized in 3 main activities:
1) Implementation and updating of the BioGenRes network of biobanks, with a focus on nationally/internationally recognized collections of animal, plant or microorganism species samples (animal and plant germplasm banks, microbial strain libraries of pathogenic/toxigenic organisms, nematodes, soil and water microflora and microorganisms used in agro-industry and food (e.g. microbial starters for fermentations)).
2) Replication (rejuvenation) and expansion of material stored in collections. For plant and microbial collections: multiplication of accessions for which a small amount of material is available and rejuvenation of accessions whose seed viability data are below the expected standards (> 85%). For animal collections of zootechnical interest: collection and freezing of genetic material of local breeds to complete sampling carried out in previous projects or expansion of the number of species and breeds stored in cryobanks.
3) Biochemical, molecular, metabolic, functional and phenotypic characterization of the material conserved in the biobanks of the BioGenRes network, also in order to carry out association studies and to identify markers associated with traits linked to production and/or adaptation to biotic and abiotic stress factors.


The project aims at the genetic improvement of innovative traits related to resistance/resilience to diseases (brucellosis, tuberculosis, paratuberculosis, transverse hemimelia), environmental sustainability (food efficiency, atmospheric emissions ), quality of productions (cheese making), enhancement of meat production as a secondary product (for example muscularity and Body Condition Score) as well as the maintenance of genetic variability of the Italian Mediterranean buffalo breed through inbreeding control and the creatio of a biobank of both male semen and embryos.


The I-BEEF project aims not only to improve the breeding plan of the Italian Limousine and Charolaise breeds by adapting it to the new sustainability and environmental selection criteria, but also to speed up the genomic characterization of 6 autochthonous beef genetic types (TGA), namely: Calvana, Mucca Pisana, Pontremolese, Sarda, Sardo Bruna, Sardo Modicana. The main objectives are biodiversity conservation and inbreeding control


The SHEEP&GOAT project aims to introduce a series of actions related to the collection and use of phenotypic and molecular data in the Italian sheep and goat farming industry, with the goal of making the breeding sustainable and competitive, and contributing to the preservation and management of its rich biodiversity.
.

